Reinkom Medical Instruments Co., Ltd
A World-Leading Supplier Of Medical Solutions
what is a laparoscopic surgical stapler
In the world of modern surgery, technological advancements have revolutionized the way procedures are performed. One such innovation is the laparoscopic surgical stapler, a crucial tool that has transformed minimally invasive surgeries.
Definition and Basics
A laparoscopic surgical stapler is a specialized medical device designed to perform stapling and cutting functions during laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves making small incisions in the patient's body and using long, thin instruments and a camera to operate. The stapler is one of the key instruments used in this type of surgery.
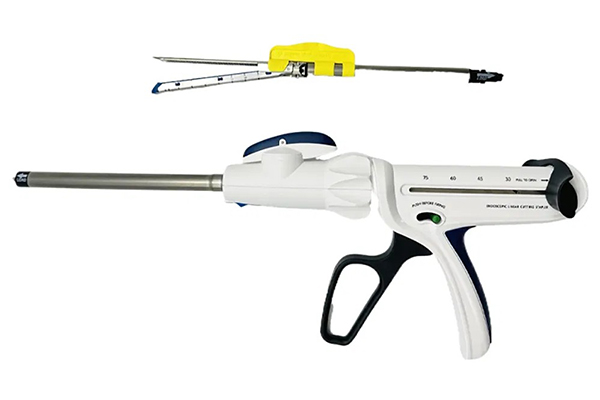

It consists of a handle, a shaft, and a stapling and cutting mechanism at the distal end. The handle is used by the surgeon to control the firing of the staples and the activation of the cutting blade. The shaft allows for the insertion of the stapler into the body through the small incisions, reaching the surgical site.
How It Works
When the surgeon squeezes the handle of the laparoscopic surgical stapler, a series of staples are deployed. These staples are typically made of stainless steel or titanium and are pre - loaded in the stapler cartridge. The staples are formed into a specific shape, usually a "B" shape, as they are driven through the tissue. This shape helps to securely fasten the tissue together, similar to how a stapler in an office binds papers.
After the staples are deployed, a cutting blade within the stapler can be activated. This blade cuts through the tissue that has been stapled, separating the targeted area from the rest of the tissue. The staples remain in place, providing hemostasis (stopping bleeding) and supporting the tissue during the healing process.
Advantages in Surgery
Hemostasis
One of the primary advantages of using a laparoscopic surgical stapler is its ability to achieve excellent hemostasis. By stapling the blood vessels in the surgical area, it effectively seals them, reducing blood loss during the procedure. This is particularly important as excessive bleeding can complicate the surgery and increase the risk of post - operative complications.
Tissue Preservation
The stapler allows for precise tissue handling. It can staple and cut tissue with minimal trauma, preserving the integrity of the surrounding tissues. This is beneficial as it helps in faster post - operative recovery and reduces the risk of damage to vital structures in the vicinity of the surgical site.
Efficiency
Laparoscopic surgical staplers significantly improve the efficiency of the surgery. The process of stapling and cutting can be done quickly and smoothly, reducing the overall operating time. This not only benefits the patient by minimizing the time under anesthesia but also allows surgeons to perform more complex procedures in a shorter period.
Applications
Laparoscopic surgical staplers are widely used in various surgical specialties. In general surgery, they are used for procedures such as bowel resection, where sections of the intestine need to be removed and the remaining ends rejoined. In gynecology, they are used for hysterectomies and tubal ligation procedures. In thoracic surgery, they are used for lung resections.
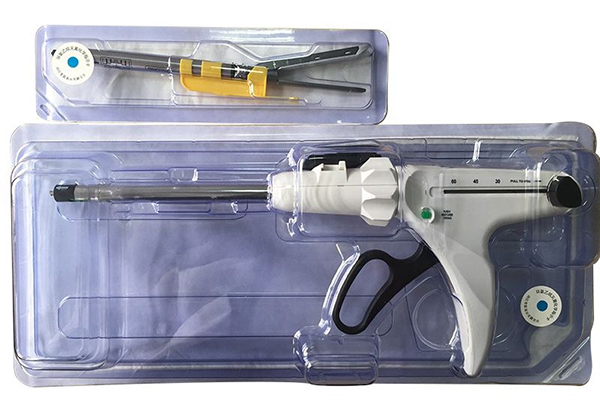
Types of Laparoscopic Surgical Staplers
There are different types of laparoscopic surgical staplers available in the market. Some are designed for linear stapling, which is useful for stapling across a straight line of tissue, such as in bowel anastomosis. Others are circular staplers, which are used for creating circular anastomoses, for example, in some types of colorectal surgeries.
In conclusion, the laparoscopic surgical stapler is an essential tool in modern minimally invasive surgery. Its ability to perform stapling and cutting functions with precision, achieve hemostasis, and preserve tissue has made it an invaluable asset for surgeons worldwide. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in the design and functionality of laparoscopic surgical staplers, leading to even better surgical outcomes for patients.